Disruption
Low-end disruption: disruptive upstart enter at the bottom of the market and take hold within an existing value network before moving up-market and attacking incumbents. steel industry (minimills) and retailing (discount retailers)
New market disruption: take hold in a completely new value network, initial customers have not used the prior generation of products and services so the incumbents ignore them. The primary competition comes from customers who would otherwise go without the products or service eg PC, Sony transistor pocket radio or small portable refrigerator.
Disruptive Innovation
Despite its popularity-in-use the core the concept of Disruptive Innovation remain widely misunderstood. There is a lot of buzz and articles but not much clarity what it defines.
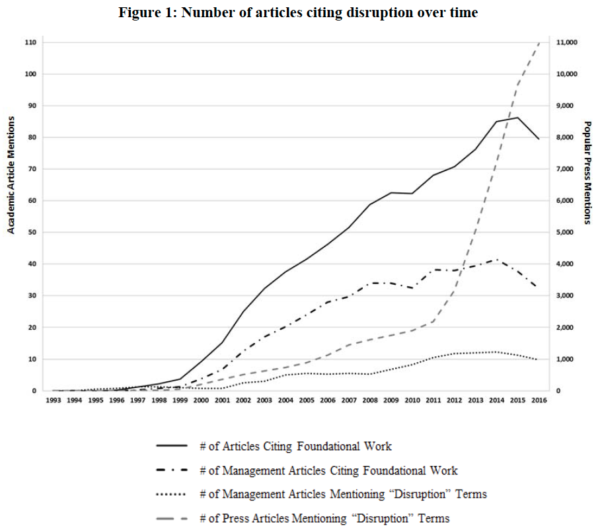
It started with wellmanaged firms that were widely lauded by analysts and the business press—yet they missed something important that precipitated their decline. Clay Christensen started analyzing the hard disk drive insdustry and with that base he continued to other industries and noticed three key factors:
- The pace of Technological progress outstrips growth in market demand for higher-performing technologies. Incumbents over-serve the market by producing more advanced, feature rich products than customer need and leave a gap at the bottom of the market between what costumers demand and what is being provided by firms.
- Innovations in technology or business model in the industry
- Sustaining Innovations: The majority of time the incumbents improve products, services and performance that mainstream customers care about. Sell more, higher margins, profit more from best existing customers.
- Disruptive Innovations: Happens less frequently and is initially inferior on performance relative to incumbents but offers other attributes (smaller, cheaper, more accessible, more conveinent) that appeal smaller groups like those left at the bottom.
- Investments in new innovations are not attractive to incumbents with existing customers and established profit models, no motivation to develop their own disruptive innovations that may lower margins, target smaller markets and introduce inferior products. But appealing for entrants with nothing to lose.
